Darvas Box Theory
The Darvas Box theory is a trading technique developed by Nicolas Darvas in the 1950s. It's a momentum-based trading strategy that uses price action to identify potential entry and exit points in the market.
How Darvas Box Works
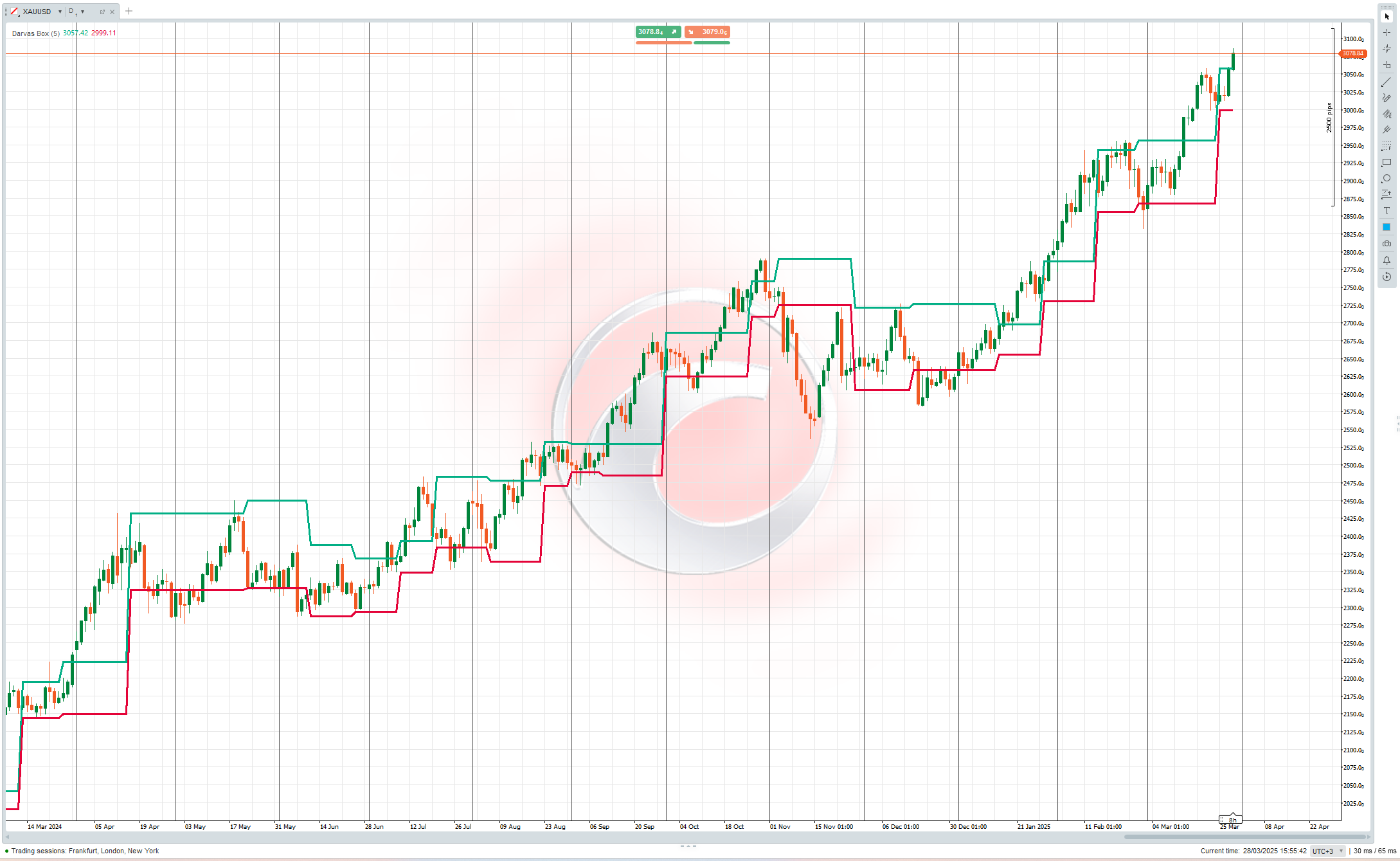
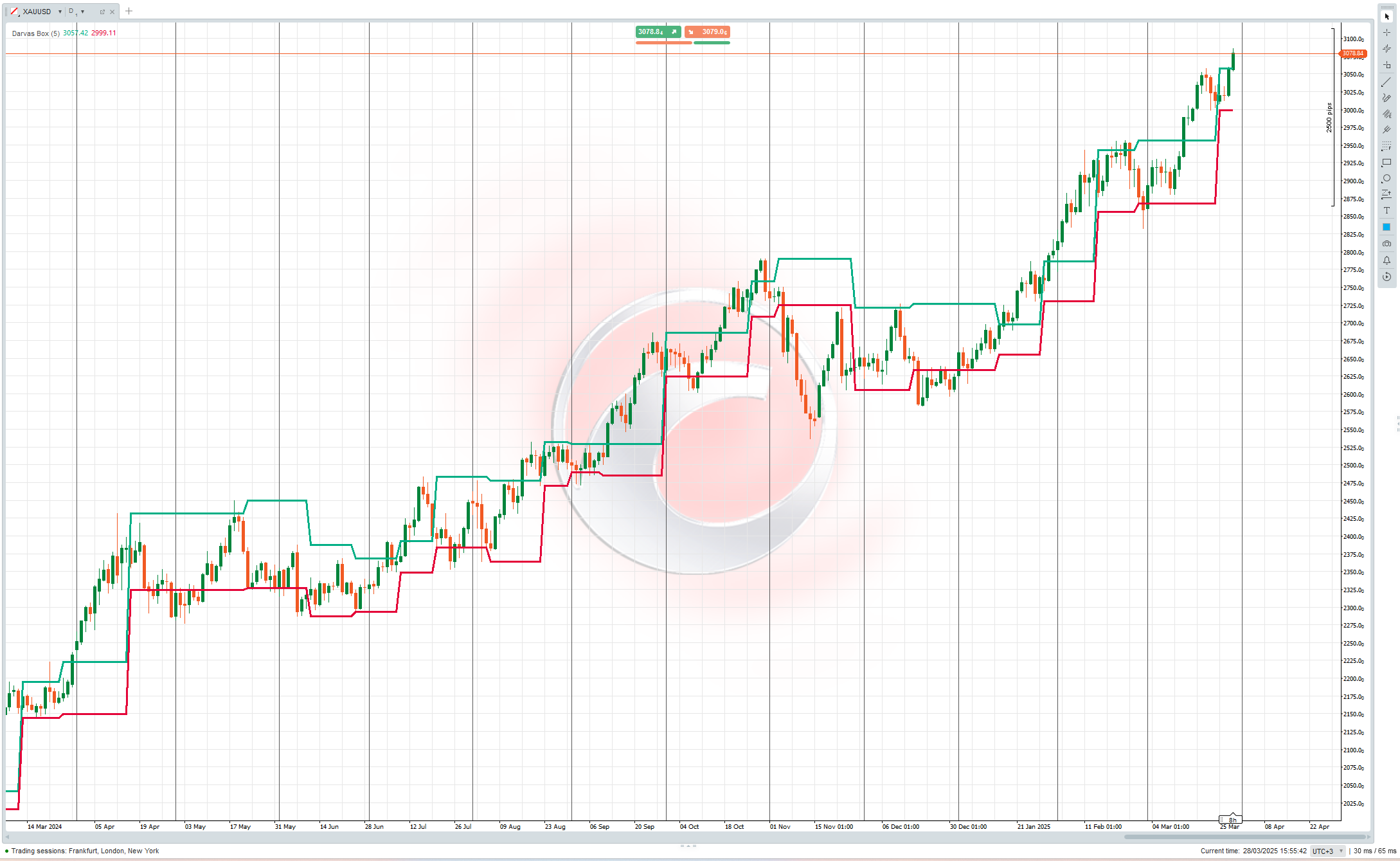
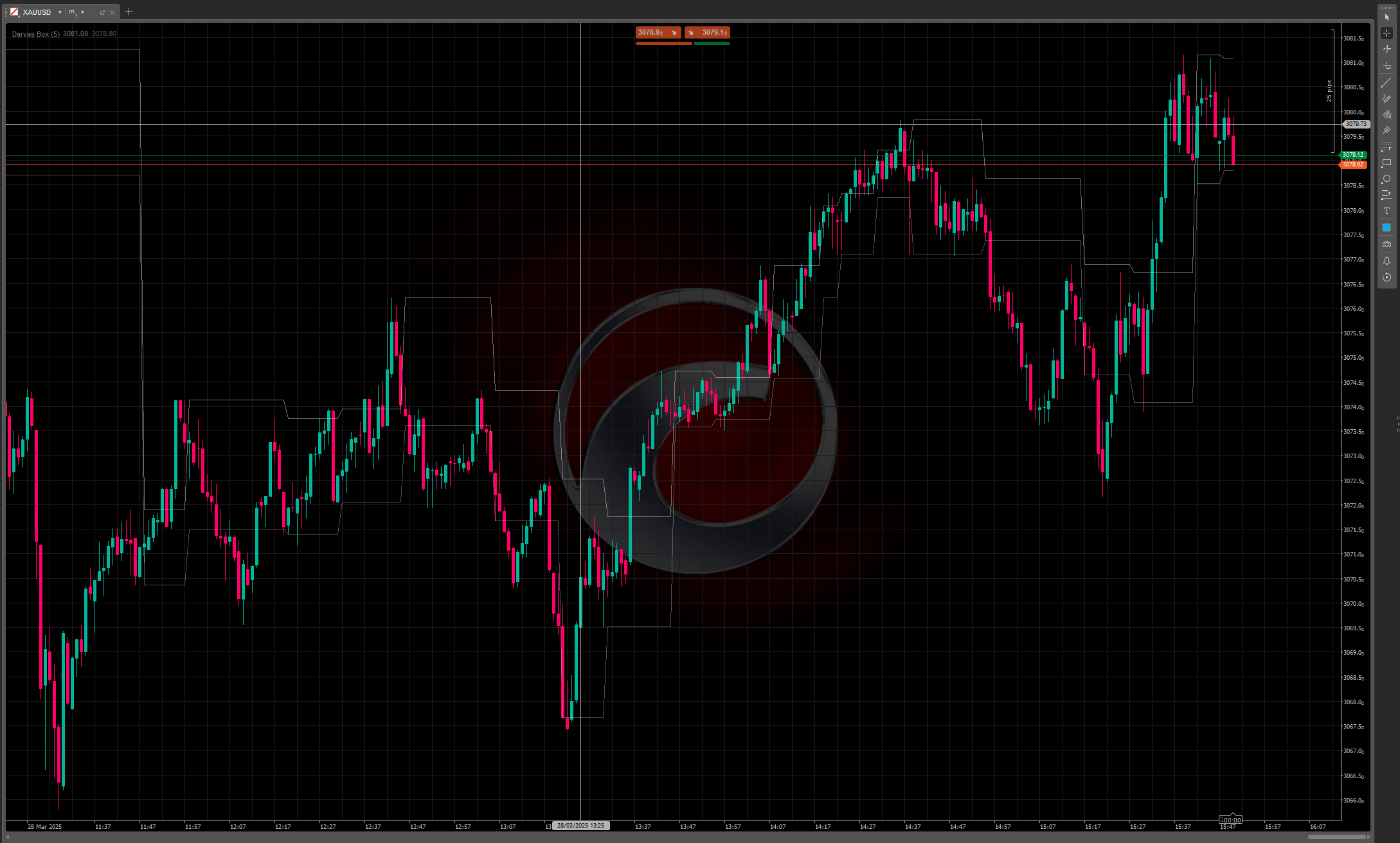
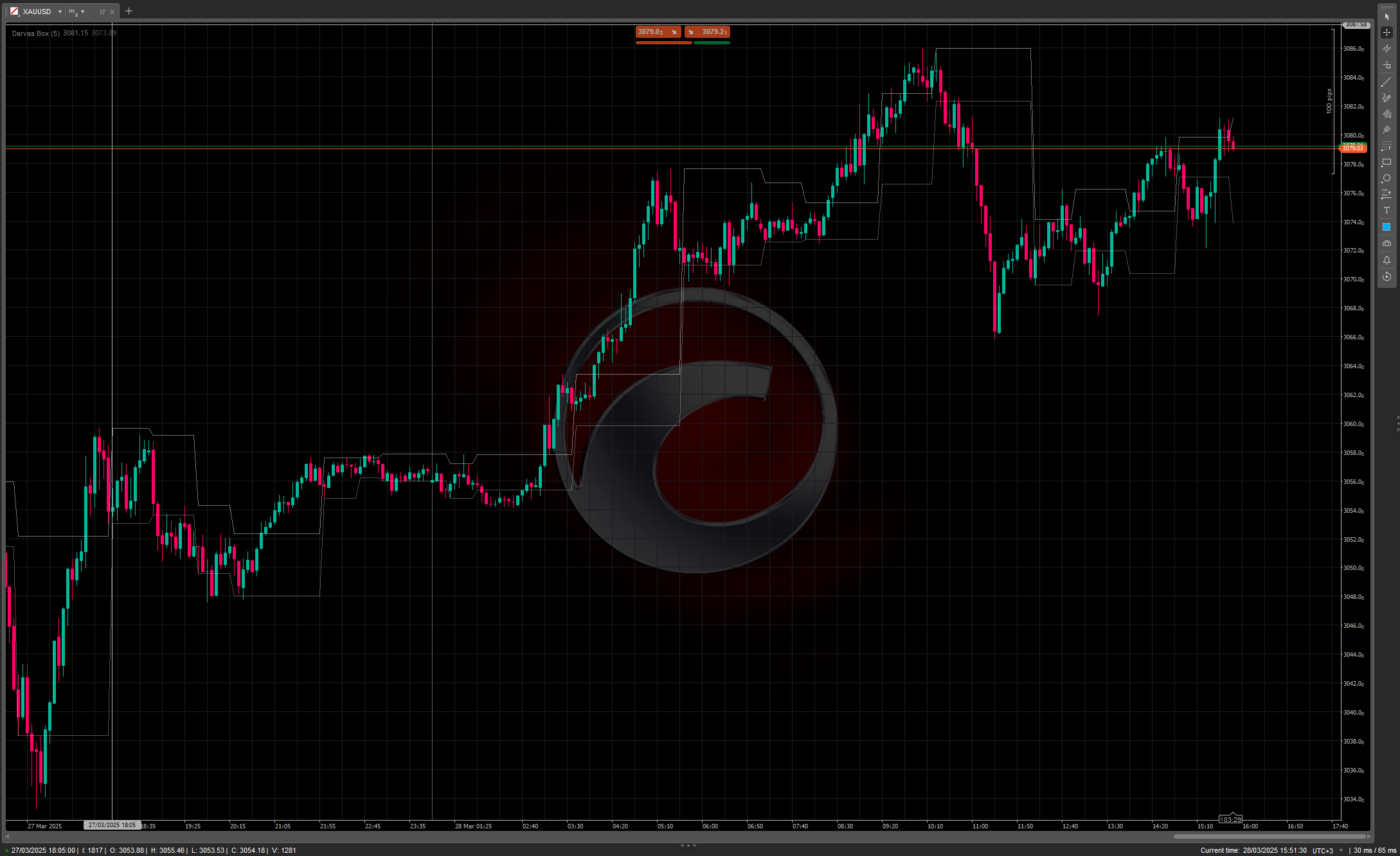
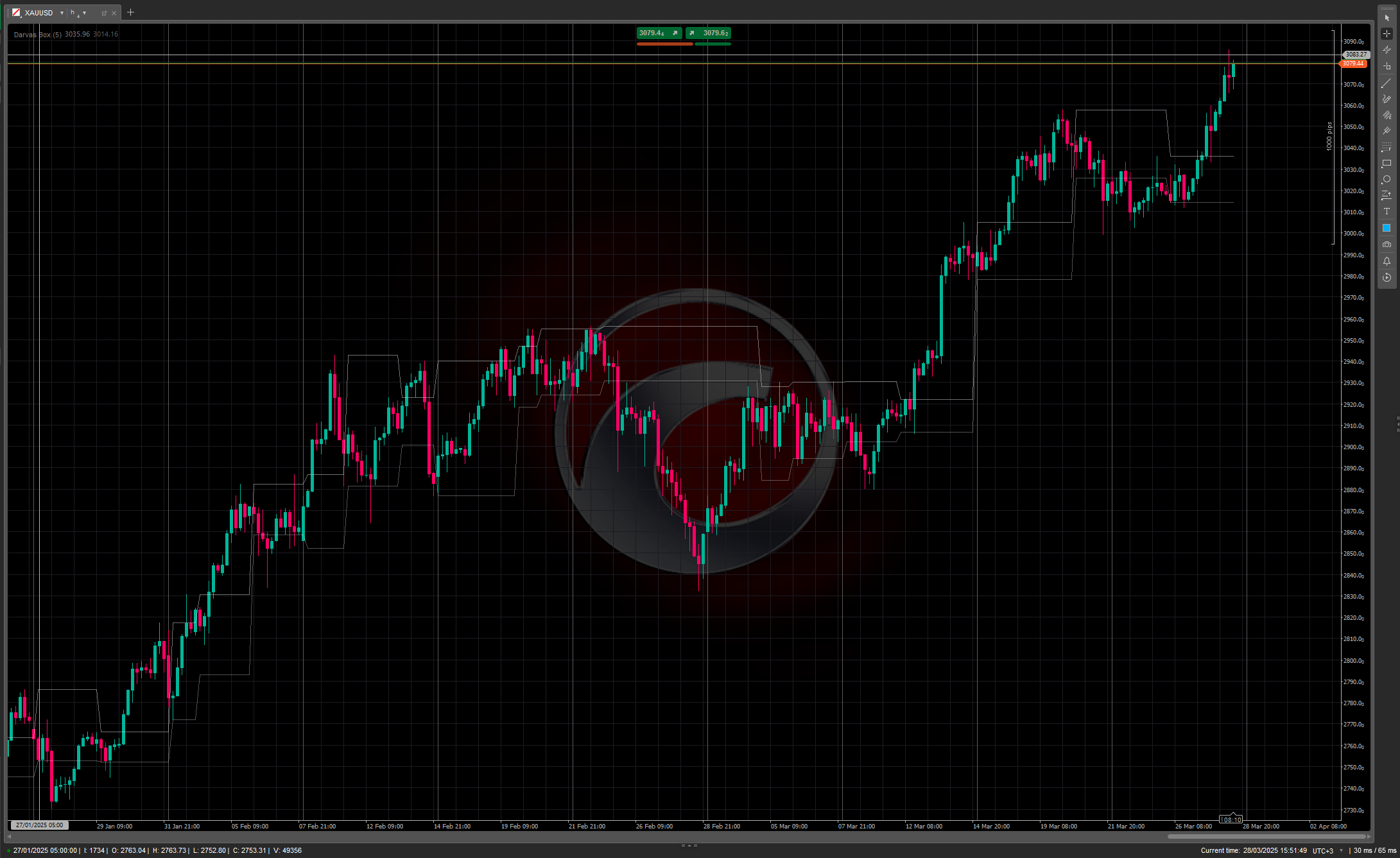
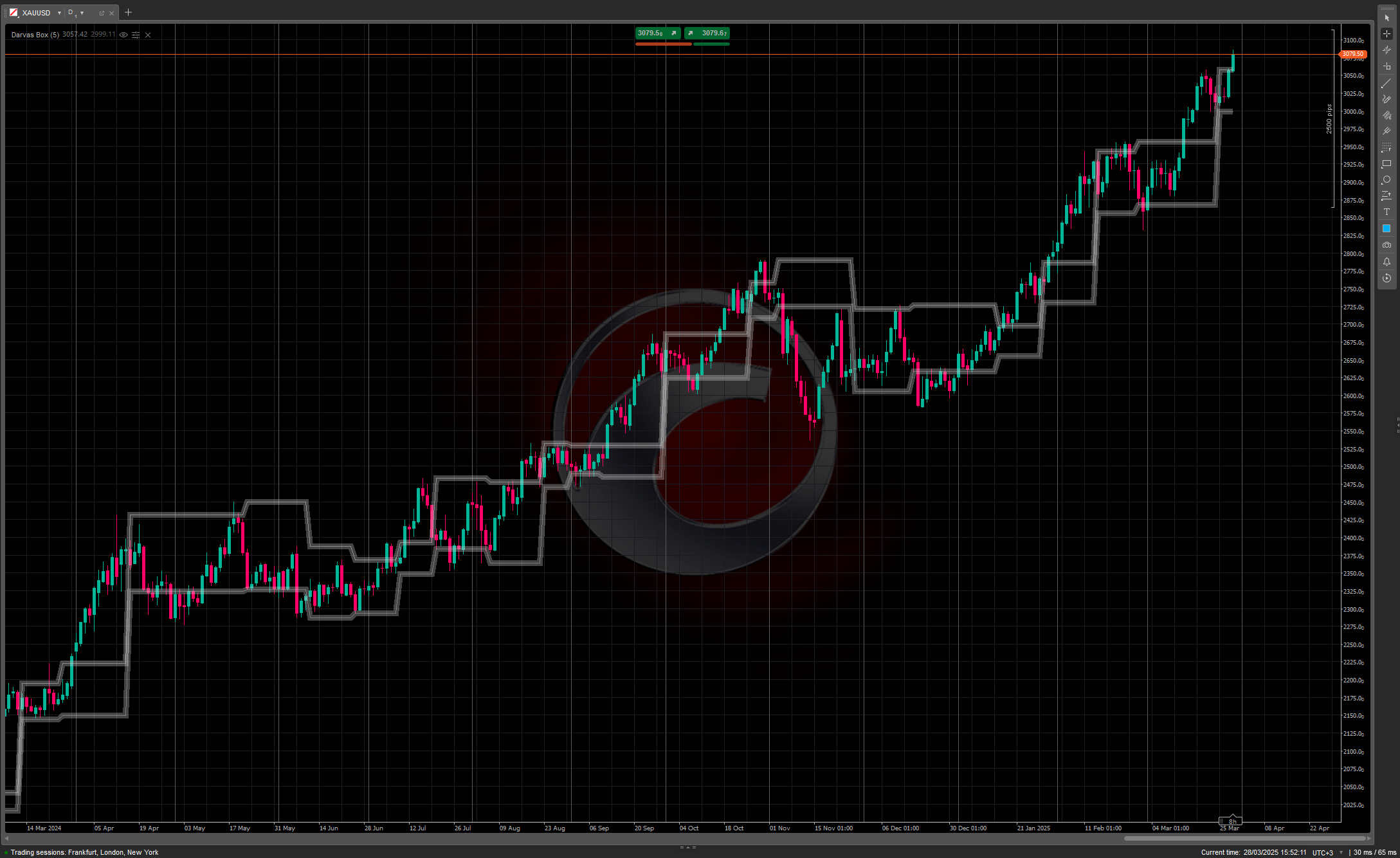
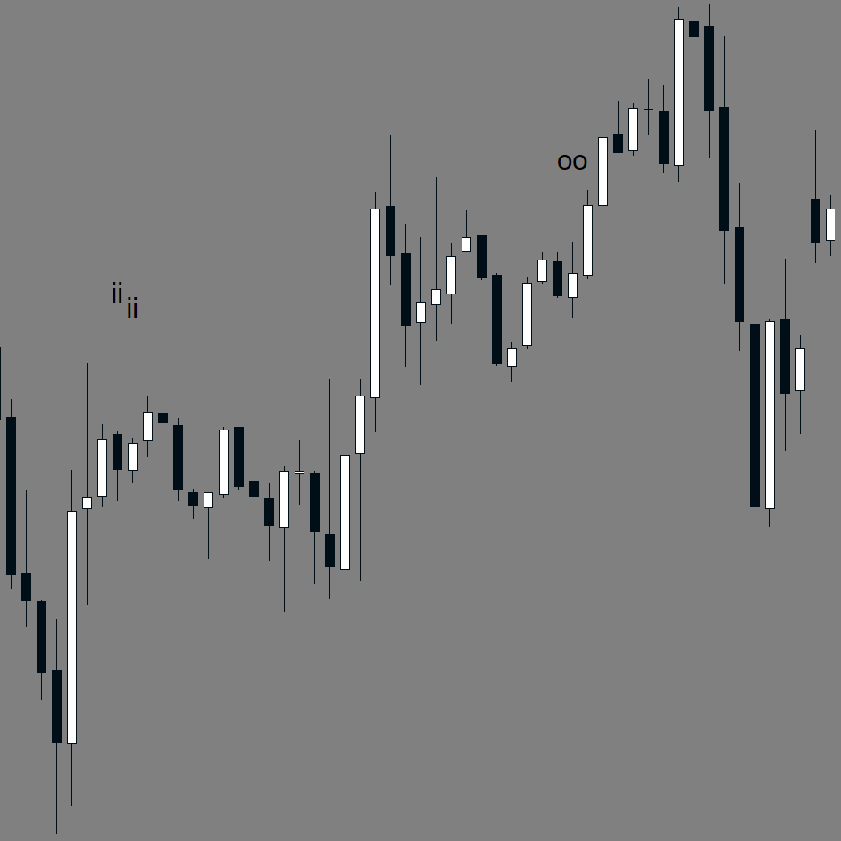
The Darvas Box method involves identifying "boxes" or trading ranges where a stock's price consolidates before breaking out. The key components include:
- Price forms a defined trading range (the "box") with clear upper and lower boundaries
- The upper boundary represents resistance, while the lower boundary acts as support
- A breakout above the box signals a potential buying opportunity
- A breakdown below the box can be used as a selling signal
Traders using this technique typically look for stocks showing increasing volume along with the price movement, as this suggests stronger momentum behind the breakout.
History of Darvas Box Theory
Nicolas Darvas (1920-1977) was a rather unusual figure in trading history. Born in Hungary, he was not a professional trader by training but rather a dancer who performed in a ballroom dance duo called "Darvas and Julia" with his half-sister.
While touring worldwide with his dance troupe in the 1950s, Darvas began experimenting with stock trading. His circumstances were unique—he often made investment decisions based only on stock tables in newspapers delivered to him in various cities during his tour.
Darvas developed his box theory through trial and error. Initially, he lost money in the markets but gradually refined his approach. Between 1956 and 1958, he reportedly turned an investment of $10,000 into over $2 million using his box method—an extraordinary feat that gained attention.
In 1960, Darvas published his methods in the book "How I Made $2,000,000 in the Stock Market," which became a classic in trading literature. The book detailed his journey and explained his box theory, bringing this approach to mainstream attention.
What made Darvas's method particularly notable was its simplicity and that it was developed by an outsider to the financial industry. He focused primarily on price action and volume rather than fundamental analysis, an approach that was somewhat novel at the time but has since influenced many technical trading systems.
The Darvas Box technique remains popular among technical traders today, particularly those who follow momentum-based strategies in trending markets.





!["[Stellar Strategies] Wave Trend Pro" logo](https://market-prod-23f4d22-e289.s3.amazonaws.com/8c93438a-6b0a-4026-93b2-0694329a3bc1_cT_cs_4141285_EURUSD_2025-04-25_17-52-31.png)


!["[Hamster-Coder] Pivot Points (Demo)" logo](https://market-prod-23f4d22-e289.s3.amazonaws.com/6a1481e2-bd00-4037-bcf0-33495594f95a_Icon300.jpg)